Table of contents
What is enterprise value?
Enterprise value (EV) represents the total value of a company. It is often confused with market capitalization, but can deviate significantly from this, especially in the case of smaller or highly indebted companies.
Enterprise value is a measure of the value of a company regardless of its financing. As the calculation appears somewhat more complicated than the calculation of market capitalization, enterprise value is used less in practice by private investors. However, EV provides more accurate information about the true value of a company than market capitalization.
The most important facts in brief
- Enterprise value represents the total value of a company
- Theoretical price at which the “naked” company would be taken over in the event of an acquisition
- More meaningful than market capitalization
How is enterprise value calculated?
Enterprise value is calculated by adding the net financial debt to the market capitalization. Net financial debt is a key figure from the balance sheet and shows the “real” debt of a company. It is the sum of current and non-current liabilities and provisions less cash and cash equivalents.
Put simply, enterprise value is essentially market capitalization adjusted for debt and cash.
Calculating enterprise value:
To illustrate, here is the calculation of Meta´s Enterprise Value as of May 26, 2025:

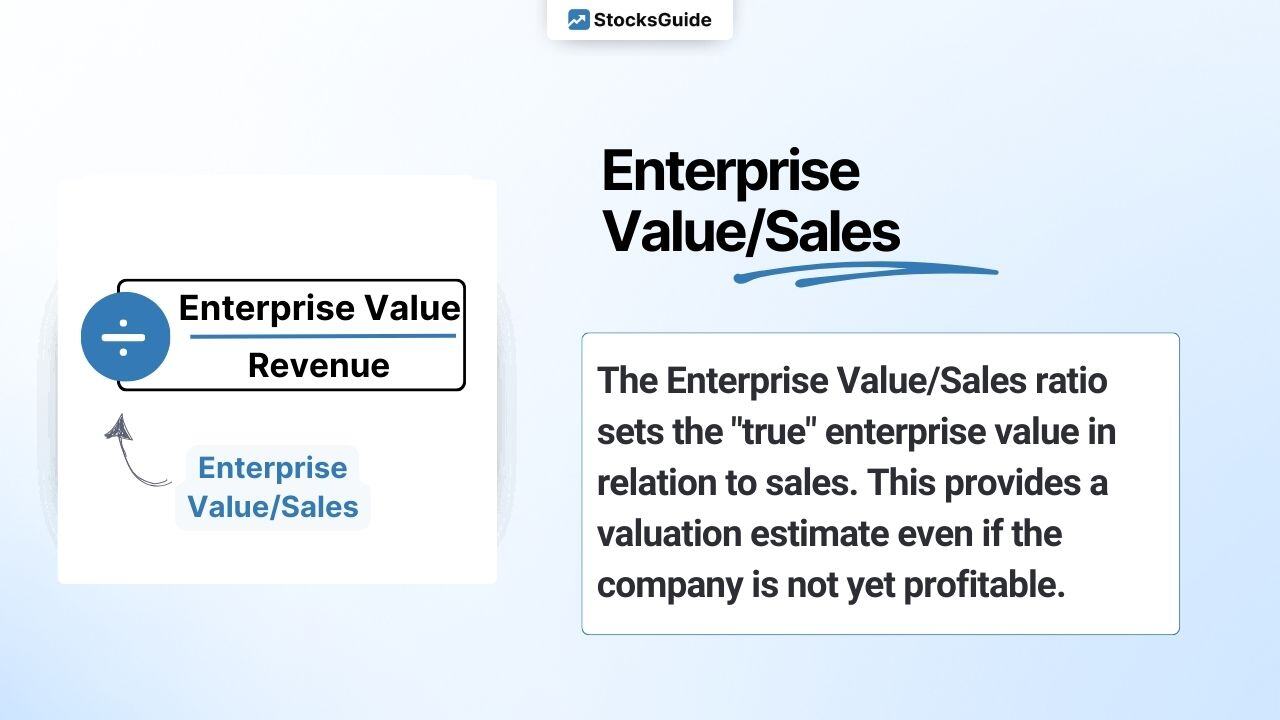
As part of the High Growth Investing strategy, this key figure is used to calculate the “EV/Sales” key figure, which represents the valuation of a company in relation to its sales.
What does enterprise value mean?
Enterprise value is the theoretical price at which the bare company would be taken over in the event of an acquisition.
For example, a strategic buyer is prepared to pay 1.5 billion US dollars for a technology company that has 500 million dollars in cash and no debt. The amount paid for the bare company (e.g. for customer relationships and technology) would then be 1.0 billion dollars, as the buyer also takes over the 500 million dollars in cash.
The largest companies in the world in terms of Enterprise Value
This table shows the companies with the highest Enterprise Valueworlwide. For a daily updated table, click here.
| Stock | Enterprise Value |
| 1. NVIDIA | $3,17t |
| 2. Apple | $2.97t |
| 3. Amazon | $2.09t |
| 4. Alphabet | $1.97t |
| 5. JPMorgan Chase & Co. | $1.71t |
| 6. Meta Platforms (Facebook) | $1.54t |
| 7. Berkshire Hathaway | $1.17t |
| 8. Goldman Sachs | $1.15t |
| 9. Broadcom | $1.13t |
| 10. Tesla | $1.06t |